-
-
Wire Harness
-
Appliance wire harness
-
New energy wiring harness
-
Industrial wiring harness
-
Automotive wiring harness
-
Medical wiring harness
MORE + -
-
Power Cord
-
China CCC
-
America UL
-
Japan PSE
-
Europe VDE/ENEC
-
British BS
-
India ISI
-
Indonesia SNI
-
Korea KC
-
Brazil INMETRO
-
Australia SAA
-
Germany ENEC
-
Italy IMQ
-
Swiss SEV
-
South Africa SABS
MORE + -
-
DC Power Cable
MORE + -
Connector
-
Power connector
-
Battery Swapping Connector
-
Energy Storage Connector
-
Solar PV Connector
-
Waterproof Connector
-
Industrial Connector
MORE + -
-
EV Charger
-
02
2025
-
01
How does fiber optic internet work?
Fiber-optic internet, often called fiber internet or simply "fiber," is a revolutionary broadband technology that transmits data at incredible speeds, reaching up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps) in some areas. This advanced technology employs fiber-optic cables, which send data at approximately 70% the speed of light. These cables are resilient to severe weather conditions and electrical interference, resulting in fewer outages compared to other types of internet connections.
Fiber-optic internet is ideal for homes or businesses with multiple devices connected simultaneously. YONGRUI Fiber Internet service enables users to:
- Upload and download files quickly.
- Enjoy smooth online gaming and video chatting.
- Back up entire hard drives to the cloud, including large photos and videos, in minutes instead of hours.
- Download a 2-hour HD movie in seconds compared to 30 minutes or more on a 20 Mbps DSL connection.
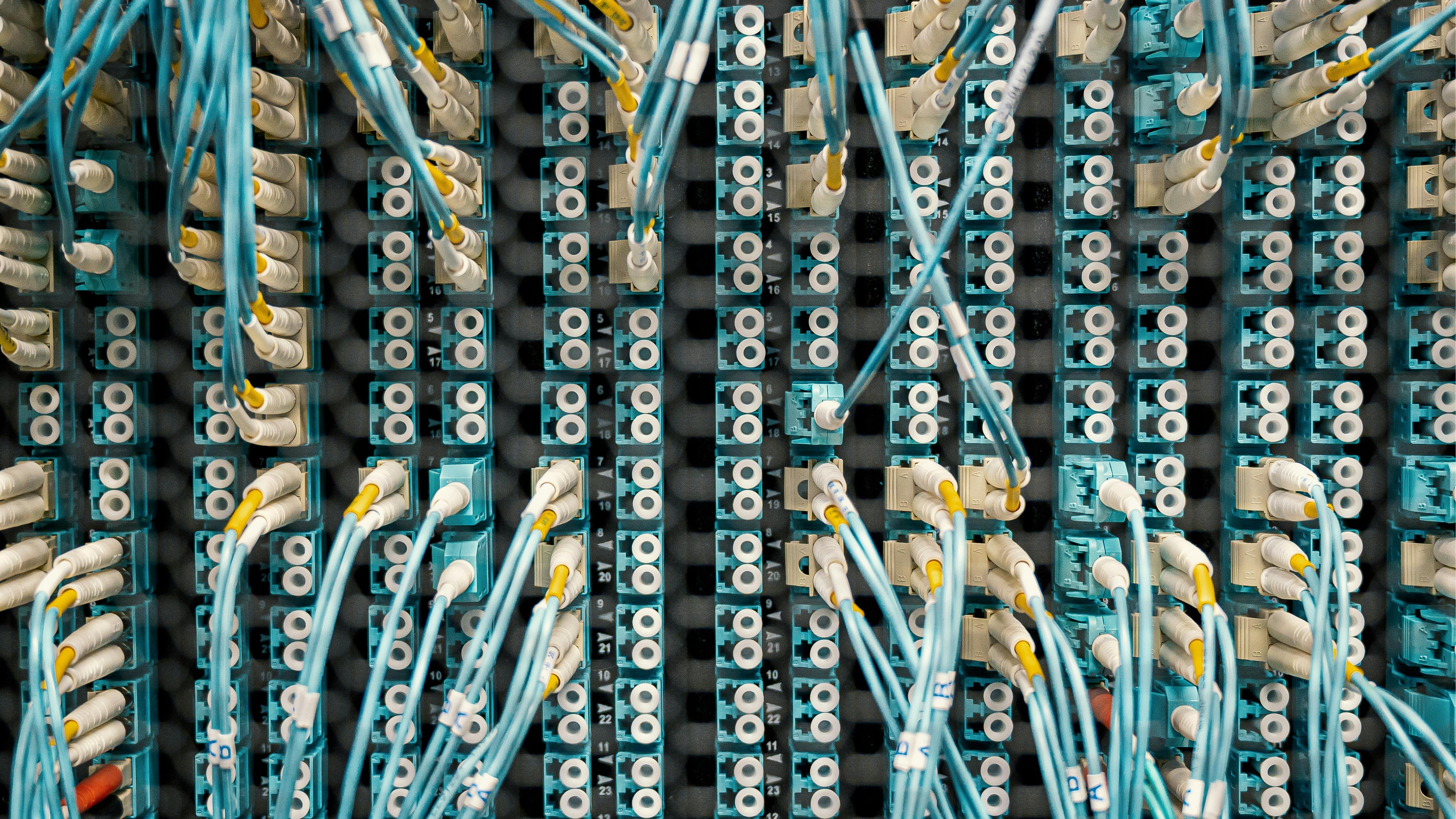
The Core of Fiber-Optic Technology
Fiber-optic internet transmits information using light rather than electricity. Key components of this technology include optical fibers and the "last mile" of the fiber-optic network.

Optical Fibers
Optical fibers are incredibly small, about 125 microns in diameter—slightly larger than a human hair. These fibers are bundled together into cables, distinct from copper-based coaxial cables. The optical fibers transmit information via pulses of laser or LED light in binary form, much like the 0s and 1s used in electronics.
The Last Mile
After these high-speed pulses of light reach their destination, they are converted into an electrical signal by an optical network terminal (ONT). This signal is then sent to the user through an Ethernet connection. The final stretch of fiber connectivity, referred to as the "last mile," connects the main fiber network line to the end user's location.
- Pure fiber connections deliver the full speed of fiber directly to homes or businesses, offering unmatched performance.
- Hybrid connections use copper cables for the "last mile," slightly reducing speed but lowering costs.
History of Fiber Optics
Fiber-optic technology may seem cutting-edge, but its origins date back to the 1970s, when it was first used in telecommunications.
- 1988: The first fiber-optic cables were laid under the ocean, connecting the U.S. and Europe.
- Today: A vast global network of fiber-optic cables spans the planet, driving progress in the Information Age.
Initially used as the "backbone" of internet networks, fiber-optic lines have increasingly replaced older copper lines. The ongoing advancements in fiber technology are making it more cost-effective to install, leading to its rapid expansion.
How Does Fiber Differ from Other Internet Types?
The main distinction lies in the medium: fiber-optic internet uses light, while other technologies rely on electrical signals.
- Dial-up: Uses copper telephone lines with speeds around 56 Kbps.
- Cable: Utilizes coaxial cables, offering speeds up to 940 Mbps for downloading.
- Fiber: Employs glass cores to deliver symmetrical speeds of up to 940 Mbps or more, ensuring superior reliability and fewer interruptions.

Benefits of Fiber-Optic Internet
Fiber-optic internet is an excellent choice for high-bandwidth households or businesses. It supports seamless streaming, gaming, and file transfers. For instance, downloading a 6.5 GB file takes approximately:
- Dial-up: 11 days
- DSL: 1-14 hours
- Cable: 1 minute to 14 hours
- Fiber: ~1 minute
With fiber, buffering becomes a thing of the past, enabling a seamless experience for smart home systems, high-resolution streaming, and data-intensive applications.
What Is Dark Fiber?
Dark fiber refers to unused fiber-optic cables laid during initial construction to save future costs. These cables remain dormant until activated for service, whereas "lit fiber" refers to the active lines delivering internet services.
Explore Fiber-Optic Internet
YONGRUI is dedicated to expanding its fiber-optic network to provide faster, more reliable internet connections. Discover the benefits of fiber technology and check if YONGRUI Fiber Internet is available in your area.
MORE NEWS
Hubei Yongrui specializes in the design, development, production, sales and service of connection harnesses (inside and outside the machine), power cords and new energy harnesses as one of the manufacturing enterprises!
©2023 Hubei Yongrui Electronic Technology Company Limited

